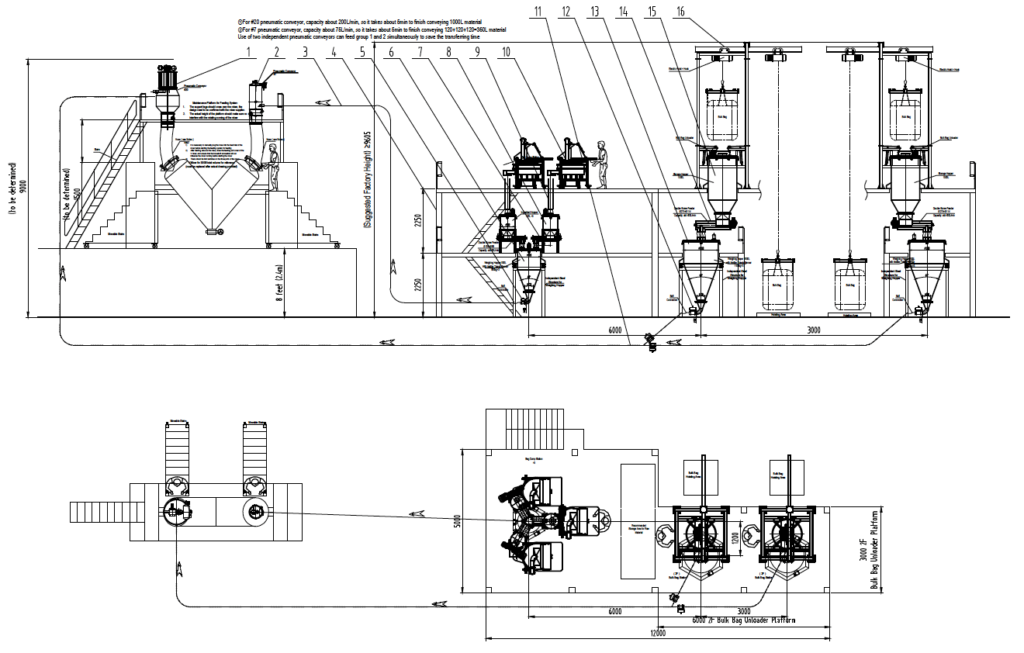
How Can You Automate Your Industrial Mixing Operation?
How Can You Automate Your Industrial Mixing Operation?
Automating an industrial mixing operation can lead to increased efficiency, consistency, and reduced labor costs. Here are steps you can take to automate your industrial mixing operation:
- Assess Your Current Process:
- Understand your current mixing process, including equipment, materials, and workflow.
- Identify areas that can benefit from automation, such as repetitive tasks, precise measurements, and consistent mixing parameters.
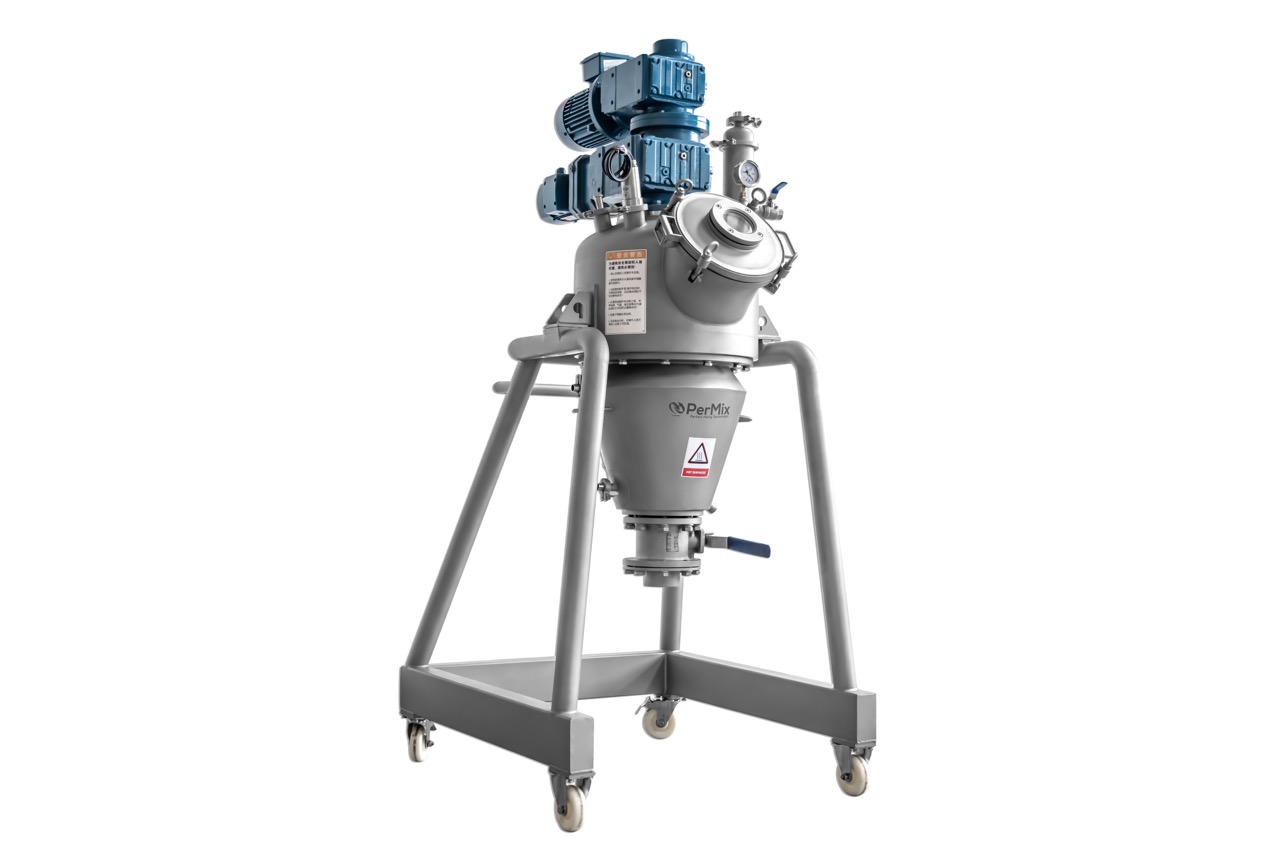
- Invest in Automated Mixing Equipment:
- Purchase or upgrade to automated mixing equipment that includes features like programmable controls, sensors, and feedback mechanisms.
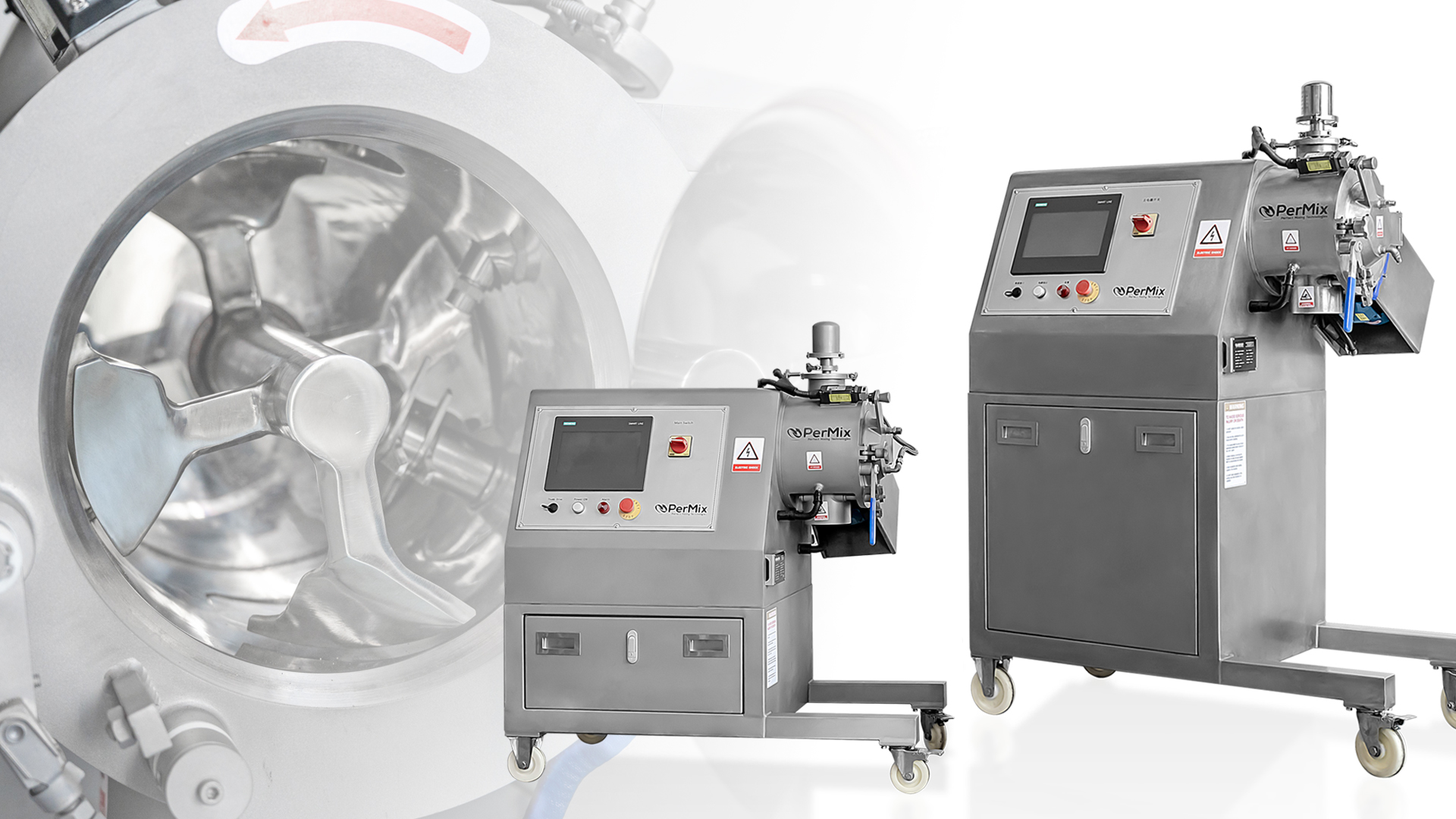
- Consider mixers with programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs) for easy monitoring and control.
- Use Sensors for Monitoring:
- Integrate sensors to monitor key parameters such as temperature, pressure, viscosity, and pH.
- Implement feedback loops to adjust mixing parameters in real-time based on sensor data.
- Implement PLCs and HMIs:
- Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) can automate the control of the mixing process. They can manage variables like speed, time, and sequence.
- Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs) allow operators to monitor and control the mixing process easily.
- Automate Material Handling:
- Integrate systems for automated material handling, such as conveyors and feeders, to ensure precise ingredient measurements and reduce manual handling.
- Recipe Management Software:
- Use recipe management software to store and recall mixing recipes easily.
- This enables quick adjustments for different formulations and ensures consistency in the final product.
- Batch Control Systems:
- Implement batch control systems to automate the sequencing of different stages in the mixing process.
- This ensures that each batch follows a standardized and optimized workflow.
- Safety Systems:
- Implement safety systems to monitor and respond to potential hazards.
- Emergency stop buttons, safety interlocks, and alarms should be integrated into the automation system.
- Training and Maintenance:
- Train operators on the new automated systems to ensure proper use and troubleshooting.
- Establish a regular maintenance schedule to keep the automated equipment in optimal condition.
- Data Logging and Analysis:
- Implement data logging systems to record key parameters during the mixing process.
- Analyze this data to identify trends, optimize processes, and predict maintenance needs.
- Integration with ERP Systems:
- Integrate your mixing operation with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems for better production planning, inventory management, and reporting.
- Continuous Improvement:
- Regularly review and assess the automated mixing process to identify opportunities for improvement.
- Stay informed about new technologies and updates in the field to keep your system up-to-date.
Remember to consult with automation experts and vendors to tailor the automation solution to your specific industrial mixing needs. Each operation is unique, and customization is often necessary to achieve the best results.
LEAN Manufacturing Considerations
Implementing LEAN manufacturing principles can significantly improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance overall productivity. Here are key considerations when incorporating LEAN principles into your industrial mixing operation:
- Value Stream Mapping:
- Begin by mapping the entire value stream of your mixing process. Identify all steps from raw material acquisition to the delivery of the final product.
- Analyze each step to determine which activities add value and which ones are non-value-added.
- Identify and Eliminate Waste:
- LEAN focuses on eliminating various forms of waste, including overproduction, excess inventory, waiting time, unnecessary transportation, overprocessing, defects, and underutilized talent.
- Evaluate each aspect of your mixing operation to identify and eliminate sources of waste.
- Standardized Work:
- Establish standardized work procedures to ensure consistency and reduce variations in the mixing process.
- Clearly define and document the best practices for each task, including mixing times, temperatures, and other relevant parameters.
- 5S Methodology:
- Implement the 5S methodology (Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, Sustain) for organizing the workspace.
- Organize tools, materials, and equipment in a systematic and efficient manner to reduce setup times and enhance overall workflow.
- Pull System:
- Implement a pull system to produce items only when they are needed in downstream processes.
- This helps minimize excess inventory and overproduction, aligning production with customer demand.
- Kanban Systems:
- Utilize Kanban systems to manage inventory levels efficiently.
- Establish visual signals that indicate when to replenish materials, ensuring a smooth and continuous flow of production.
- Continuous Flow:
- Aim to create a continuous flow in the mixing process to minimize batch sizes and reduce waiting times.
- Streamlining the flow can lead to more predictable and efficient production.
- Cross-Training and Flexibility:
- Cross-train employees to perform multiple tasks within the mixing operation.
- This enhances flexibility, allowing you to adapt quickly to changing production demands.
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM):
- Implement TPM practices to ensure that equipment is well-maintained and downtime is minimized.
- Regularly schedule preventive maintenance to keep equipment in optimal condition.
- Kaizen (Continuous Improvement):
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement (Kaizen) among your team.
- Encourage employees to identify and suggest improvements to the mixing process regularly.
- Employee Involvement and Empowerment:
- Involve employees in the decision-making process and encourage them to contribute ideas for improvement.
- Empower employees to take ownership of their work areas and processes.
- Quality Control:
- Implement robust quality control measures to detect and address defects early in the process.
- Use feedback mechanisms to continuously improve product quality.
Remember that LEAN manufacturing is a continuous journey of improvement. Regularly review your processes, gather feedback, and make adjustments to ensure sustained efficiency gains over time.